“We must begin with the basic facts and figures that describe our access to outer space. It is true that 2024 has ushered in a new era, and January 2024 was the busiest start to a year since 1957 in terms of orbital launches. While we continue to break new ground and build new capabilities, like the SpaceX Starship, we are still at the early stages of the new outer space age…. while growing, our access to outer space is still patchy with only a few consistent players.”
Financing the Race to Space, 2024
This post highlights some of the arguments I make in the Introduction of my latest book, Financing the Race to Space. You can learn more through the books as well as the many different tabs on this site.
Other Posts
As we witness the mindless destruction of our ecosystem and the promise of a future landing on some non-habitable planet we plan to terraform, our survival and the survival of our children and their children depends on our ability to authentically assess and understand where we stand on this sustainability/expansion journey.
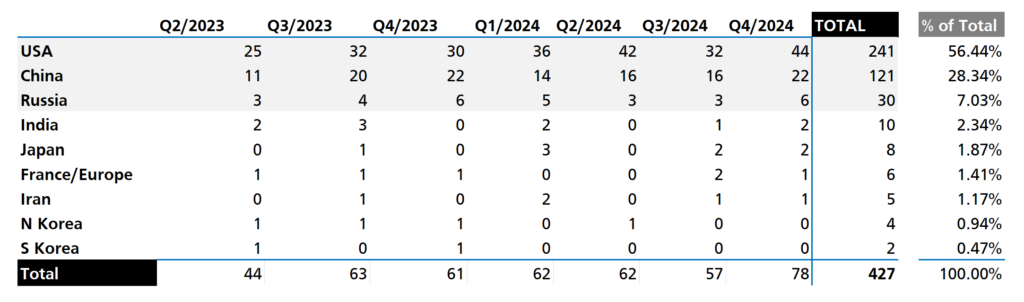
USA, China, and Russia were responsible for 91.8% of all orbital launches from Earth between Q2/2023 & Q4/2024. India, the fourth power in outer space, is at 2.34%, followed by hashtag #Japan at 1.87%. France Europe is at 1.41%, then comes Iran at 1.17%, North Korea at 0.94%, and South Korea at 0.47%.
📰 The tables list
🚀 All the countries that have achieved orbital launches from Earth in those quarters. These are based on where the provider or responsible entity is headquartered, not the physical location of the launch. Often these are one and the same.
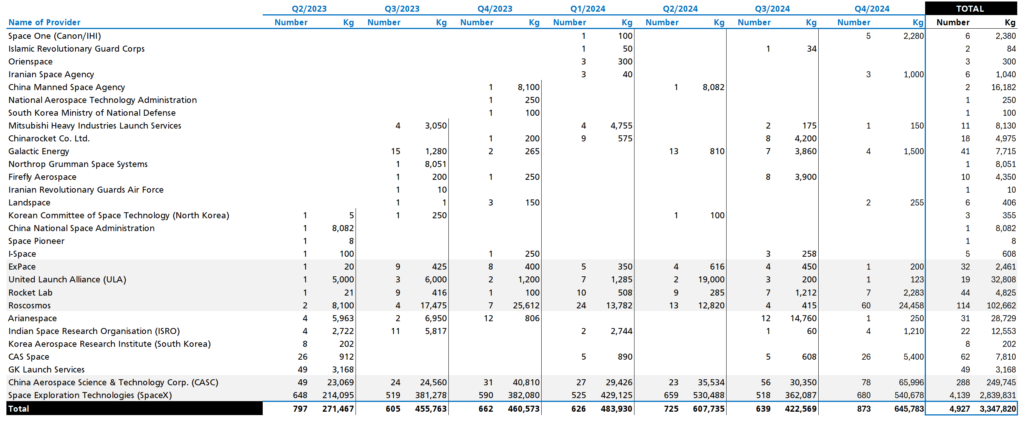
🚀 And all the providers, and the number of spacecraft and upmass they have sent to orbit, between Q2/2023 to Q4/2024. The providers are first ranked according to the number of spacecraft they sent to orbit in Q2/2023.
🛰️ While these numbers do not provide any insight as to what is being sent to orbit (vast majority are satellites), they do provide an accurate picture of outer space access capability. The greyed out rows identify those countries/providers that have been active in all the seven quarters depicted.
The list reveals the unique constitution/composition of humanity’s ability to reach beyond the atmosphere, or Low Earth Orbit, Medium Earth Orbit, and Geostationary Orbit.
In the providers list, you can also observe the geopolitical and military backdrop of this composition. As FYI, the United States Space Force is responsible for 93 lift-offs in 2024 (88 SpaceX, 5 United Launch Alliance).
Basically, we are destroying our one and only home from under our own feet at an alarming rate, while we are still at the early stages of our expansion in outer space.
Moreover, much of our ‘expansion’ in outer space is about launching satellites to deliver goods and services on Earth, or for military and security purposes to ‘defend’ the species from itself.
Do we realise where this is going?
Our sustainability and expansion in space are intricately related.
If you would like to gain further insights, please feel free to get in touch through the Space Value Foundation site or comment below.
hashtag#space hashtag#risk hashtag#time hashtag#money hashtag#finance hashtag#sustainability hashtag#expansion
Countries responsible for orbital launches, and Spacecraft and Upmass carried to Orbit by Provider, between Q2/2023 to Q4/2024
Source: Compiled by Author from BryceTech Briefings
https://lnkd.in/epgvKbdf
The tax and debt focus of the new 'rebuilding Britain' budget is the direct outcome of our current monetary and fiscal framework and the state of public finances. As such, I believe it should be treated as a stop loss budget, even though an expensive one for many.
To launch Britain into orbit, we must be able to reinvent the policy matrix that has led us to our current predicament. While discipline is a MUST, our current financial value framework and monetary architecture can and should be reformed.
As I have discussed in previous posts, and I elaborate in the book, if Britain wants to transcend and conquer the challenges of the last 14 years, achieve growth, and launch itself to orbit, it must first address the shortcomings of our financial value framework, mathematics, and monetary architecture.










